Recycling by-product
- home
Sustainability
Eco-Friendly Management
Recycling by-product
- Recycling of Hot Power Plant Wastewater
- Carbon Capture & Storage (CCS)
- Coal Ash & Recycling of Gypsum
KOMIPO is making continuous efforts to expand recycling of by-products occurring during operation of its power plants,, including diversification of demand applications, promotion of R&D and identification of new usages. Regarding the hot wastewater discharged from its power plants, KOMIPO is promoting a wide variety of projects for utilization as one of the eight new energy industry models announced by the government.
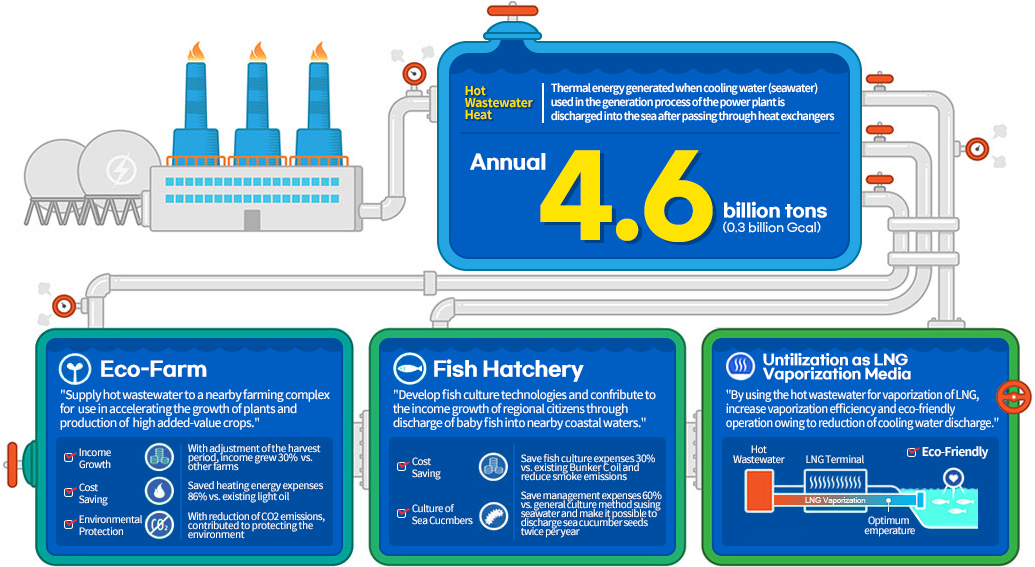
- Hot Wastewater Heat
- Thermal energy generated when cooling water (seawater) used in the generation process of the power plant is discharged into the sea after passing through heat exchangers
- Annual 4.6 billion tons (0.3 billion Gcal)
- Eco-Farm
- 'Supply hot wastewater to a nearby farming complex for use in accelerating the growth of plants and production of high added-value crops.'
-
- Income Growth : With adjustment of the harvest period, income grew 30% vs. other farms
- Cost Saving : Saved heating energy expenses 86% vs. existing light oil
- Environmental Protection : With reduction of CO2 emissions, contributed to protecting the environment
- Fish Hatchery
- 'Develop fish culture technologies and contribute to the income growth of regional citizens through discharge of baby fish into nearby coastal waters.'
-
- Cost Saving : Save fish culture expenses 30% vs. existing Bunker C oil and reduce smoke emissions
- Culture of Sea Cucumbers : Save management expenses 60% vs. general culture method using seawater and make it possible to discharge sea cucumber seeds twice per year
- Utilization as LNG Vaporization Media
- 'By using the hot wastewater for vaporization of LNG, increase vaporization efficiency and eco-friendly operation owing to reduction of cooling water discharge.'
- Eco-Friendly : Hot Wastewater, LNG Terminal, Optimum Temperature
1. R&D for Utilizing Wastewater in Farming Field: Boryeong Power Generation Site Division, Jeju Power Generation Site Division
KOMIPO is pursuing a pan-ministerial cooperation task (tentative name: 'Eco-Farm') for development of technologies utilizing hot wastewater in the farming field. This project is designed to utilize the hot wastewater discharged from power plants as heating energy and develop an eco-friendly smart greenhouse system that controls crop growing environments with IoT. Jointly with the Ministry of Agriculture, Food & Rural Affairs and Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, KOMIPO is also engaged in a project to supply the hot wastewater to a flower complex near the Jeju TPP to utilize for greenhouse heating.
Eco-Farm


2. Operation of Fish Hatchery: Boryeong Power Generation Site Division
The site division invested about ?6.9 billion in 2015 to establish a fish hatchery utilizing the hot wastewater discharge from its power plants and now discharges baby fish into nearby coastal waters. The hatchery can save energy expenses for heating water by using the hot wastewater and contributes to the income growth of fishermen through increase of fishery resources by releasing the baby fish produced at lower cost into coastal areas adjacent to the power plants. Therefore, it is a project welcomed by fishermen.
Fish Hatchery


Fish Hatchery Completion Ceremony & Baby Fish Release Event


3. Provision of Hot Wastewater to LNG Terminal for Vaporization Heat
The Boryeong Power Generation Site Division has concluded an MOU to provide about 370 million tons of hot wastewater annually to the Boryeong LNG Terminal, located near the division, as a heating supply source for the terminal's LNG storage facility. The terminal will utilize the hot wastewater as LNG vaporization media.
To treat CO2 occurring in the course of coal combustion, KOMIPO installed a 10MW-class CCS (Carbon Capture & Storage) facility at its Boryeong Power Generation Site Division. The company is proceeding with R&D to reuse the compressed and stored CO2 for industry or farming. Starting in June 2017, the site division plans to supply about 50,000 tons of liquefied CO2 (purity: 99.99%) annually for production of carbonated beverages and as a photosynthesis media in the farming field. This has great significance in that KOMIPO has secured domestic self-reliance for CO2 capture and commercialization technologies. It plans to expand the CCS capacity to 100MW class for verification.


Coal ash occurring in the course of coal combustion is being recycled as a major construction resource, such as for remicon (ready mixed concrete) mixture and cement raw material. Meanwhile, the gypsum produced from the DeSOx facility is being 100% recycled as material for gypsum board, etc.
Coal Ash Types (Fly Ash, Bottom Ash)



Recycled Products